Features¶
Overview¶
With the great success of deep learning,DNN-based techniques have been widely used in CTR prediction task.
DNN based CTR prediction models usually have following 4 modules:
Input,Embedding,Low-order&High-order Feature Extractor,Prediction
- Input&Embedding
The data in CTR estimation task usually includes high sparse,high cardinality categorical features and some dense numerical features.
Since DNN are good at handling dense numerical features,we usually map the sparse categorical features to dense numerical throughembedding technique.
For numerical features,we usually applydiscretizationornormalizationon them.
- Feature Extractor
Low-order Extractor learns feature interaction through product between vectors.Factorization-Machine and it’s variants are widely used to learn the low-order feature interaction.
High-order Extractor learns feature combination through complex neural network functions like MLP,Cross Net,etc.
Feature Columns¶
SparseFeat¶
SparseFeat is a namedtuple with
signature SparseFeat(name, vocabulary_size, embedding_dim, use_hash, vocabulary_path, dtype, embeddings_initializer, embedding_name, group_name, trainable)
- name : feature name
- vocabulary_size : number of unique feature values for sparse feature or hashing space when
use_hash=True - embedding_dim : embedding dimension
- use_hash : default
False.IfTruethe input will be hashed to space of sizevocabulary_size. - vocabulary_path : default
None. TheCSVtext file path of the vocabulary table used bytf.lookup.TextFileInitializer, which assigns one entry in the table for each line in the file. One entry contains two columns separated by comma, the first is the value column, the second is the key column. The0value is reserved to use if a key is missing in the table, so hash value need start from1. - dtype : default
int32.dtype of input tensor. - embeddings_initializer : initializer for the
embeddingsmatrix. - embedding_name : default
None. If None, the embedding_name will be same asname. - group_name : feature group of this feature.
- trainable: default
True.Whether or not the embedding is trainable.
DenseFeat¶
DenseFeat is a namedtuple with signature DenseFeat(name, dimension, dtype, transform_fn)
- name : feature name
- dimension : dimension of dense feature vector.
- dtype : default
float32.dtype of input tensor. - transform_fn : If not
None, a function that can be used to transform values of the feature. the function takes the input Tensor as its argument, and returns the output Tensor. (e.g.lambda x: (x - 3.0) / 4.2).
VarLenSparseFeat¶
VarLenSparseFeat is a namedtuple with
signature VarLenSparseFeat(sparsefeat, maxlen, combiner, length_name, weight_name,weight_norm)
- sparsefeat : a instance of
SparseFeat - maxlen : maximum length of this feature for all samples
- combiner : pooling method,can be
sum,meanormax - length_name : feature length name,if
None, value 0 in feature is for padding. - weight_name : default
None. If not None, the sequence feature will be multiplyed by the feature whose name isweight_name. - weight_norm : default
True. Whether normalize the weight score or not.
Models¶
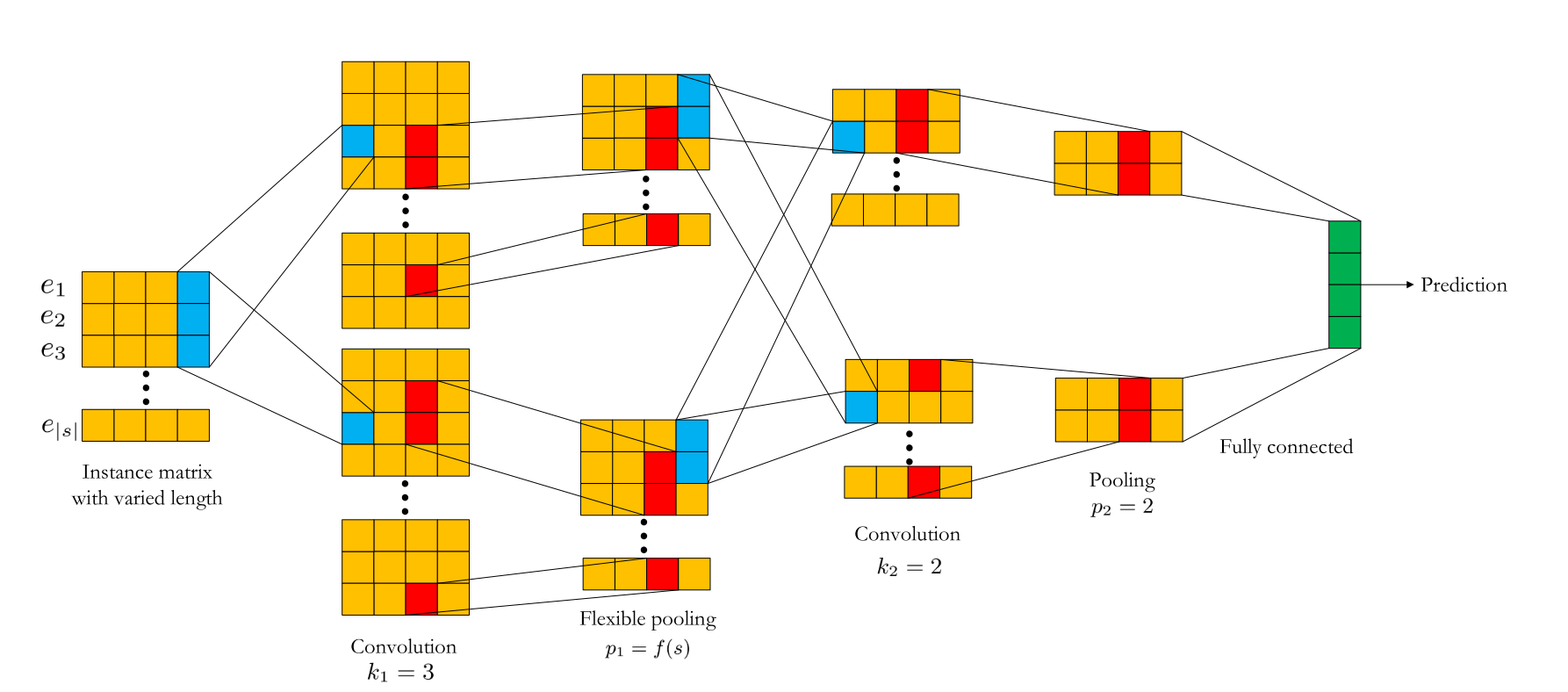
CCPM (Convolutional Click Prediction Model)¶
CCPM can extract local-global key features from an input instance with varied elements, which can be implemented for not only single ad impression but also sequential ad impression.
CCPM Model API CCPM Estimator API
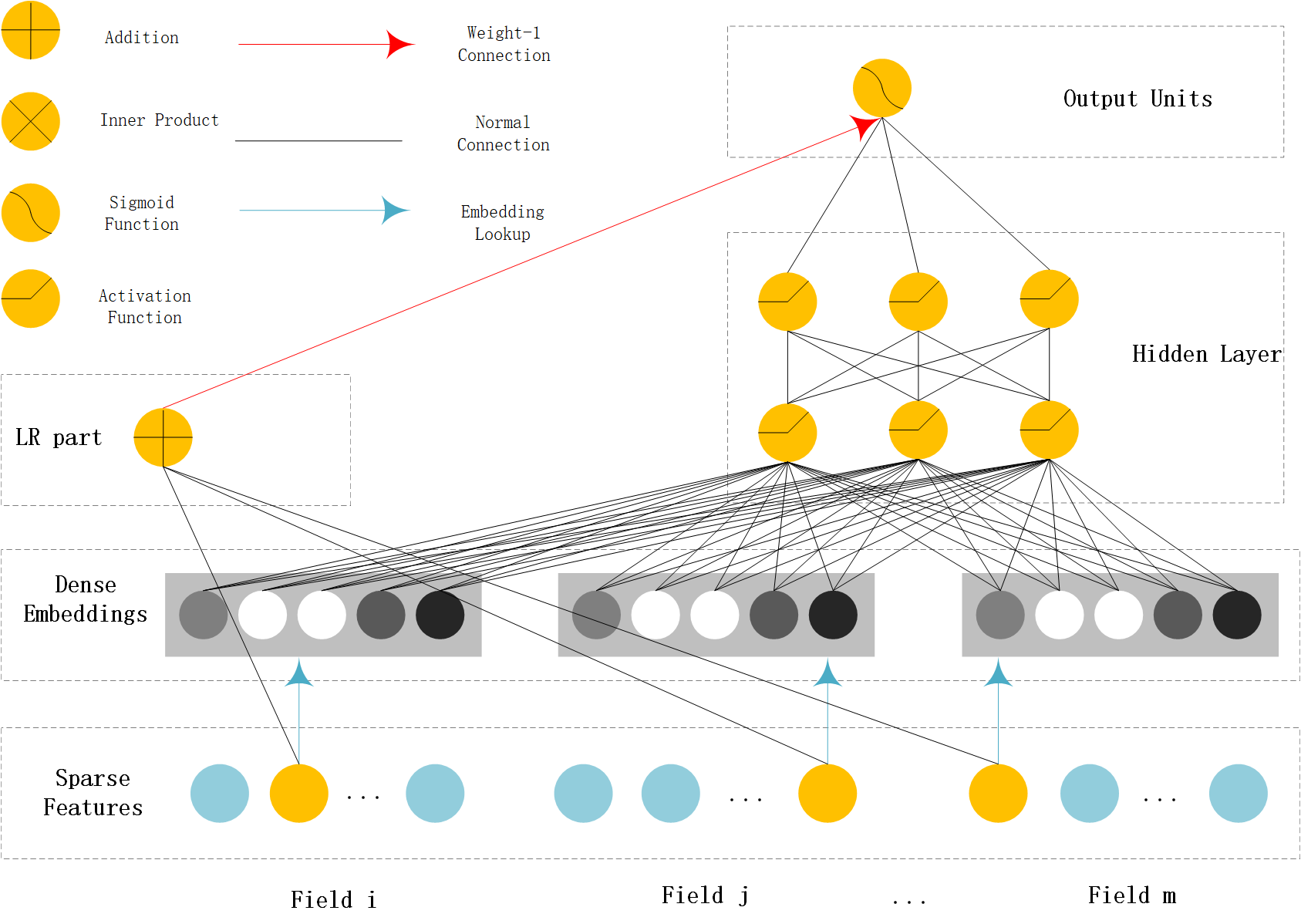
FNN (Factorization-supported Neural Network)¶
According to the paper,FNN learn embedding vectors of categorical data via pre-trained FM. It use FM’s latent vector to initialiaze the embedding vectors.During the training stage,it concatenates the embedding vectors and feeds them into a MLP(MultiLayer Perceptron).
FNN Model API FNN Estimator API
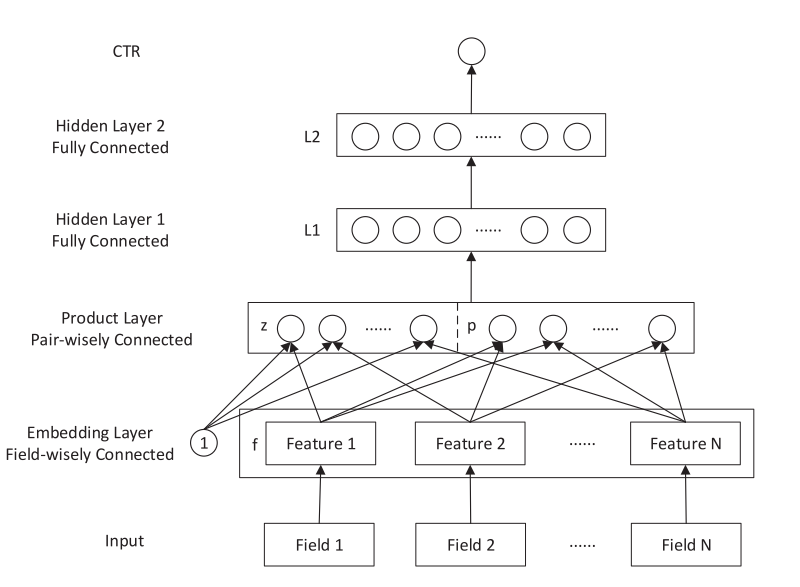
PNN (Product-based Neural Network)¶
PNN concatenates sparse feature embeddings and the product between embedding vectors as the input of MLP.
PNN Model API PNN Estimator API
Wide & Deep¶
WDL’s deep part concatenates sparse feature embeddings as the input of MLP,the wide part use handcrafted feature as input. The logits of deep part and wide part are added to get the prediction probability.
WDL Model API WDL Estimator API
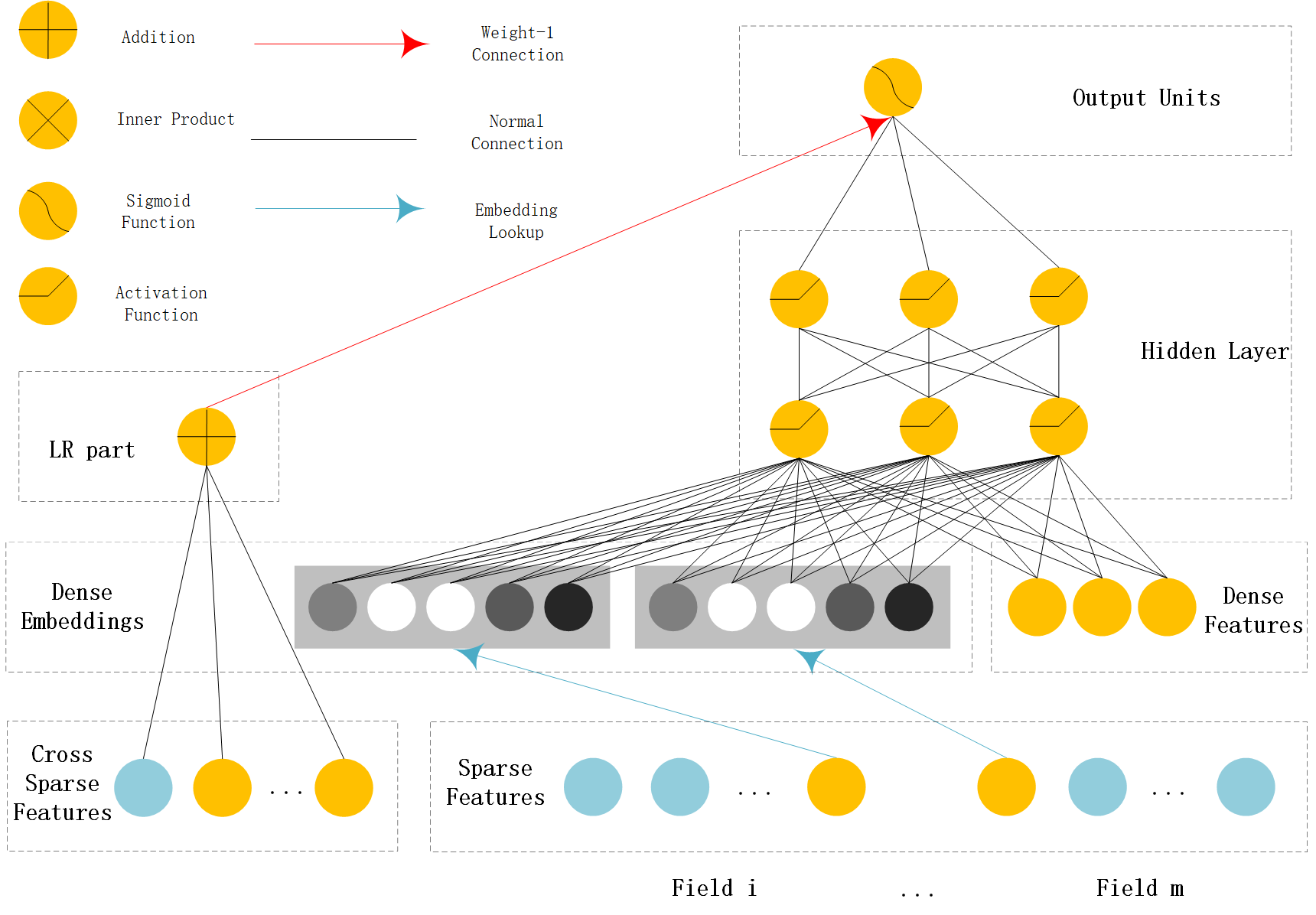
DeepFM¶
DeepFM can be seen as an improvement of WDL and FNN.Compared with WDL,DeepFM use FM instead of LR in the wide part and use concatenation of embedding vectors as the input of MLP in the deep part. Compared with FNN,the embedding vector of FM and input to MLP are same. And they do not need a FM pretrained vector to initialiaze,they are learned end2end.
DeepFM Model API DeepFM Estimator API
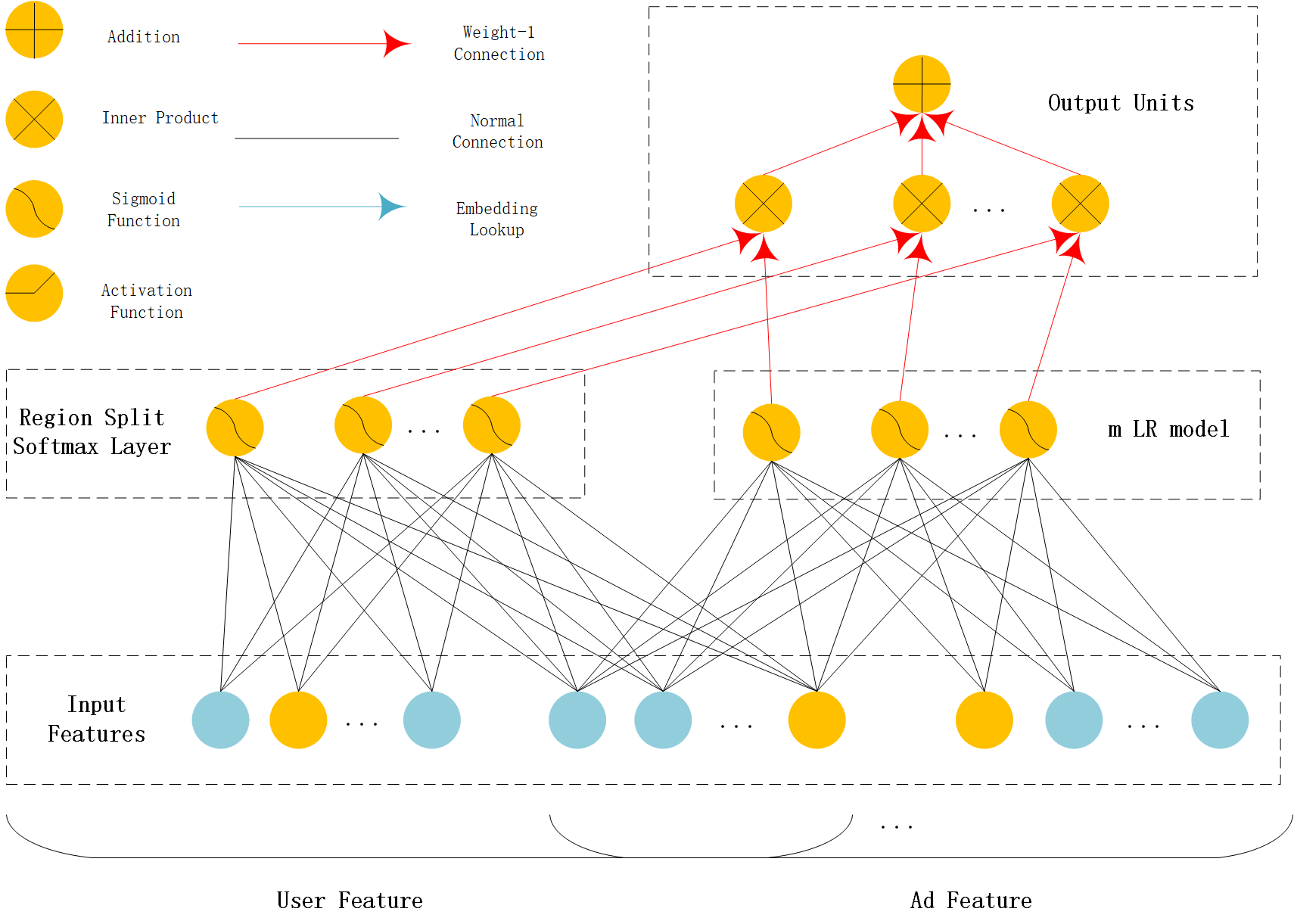
MLR(Mixed Logistic Regression/Piece-wise Linear Model)¶
MLR can be viewed as a combination of $2m$ LR model, $m$ is the piece(region) number. $m$ LR model learns the weight that the sample belong to each region,another m LR model learn sample’s click probability in the region. Finally,the sample’s CTR is a weighted sum of each region’s click probability.Notice the weight is normalized weight.
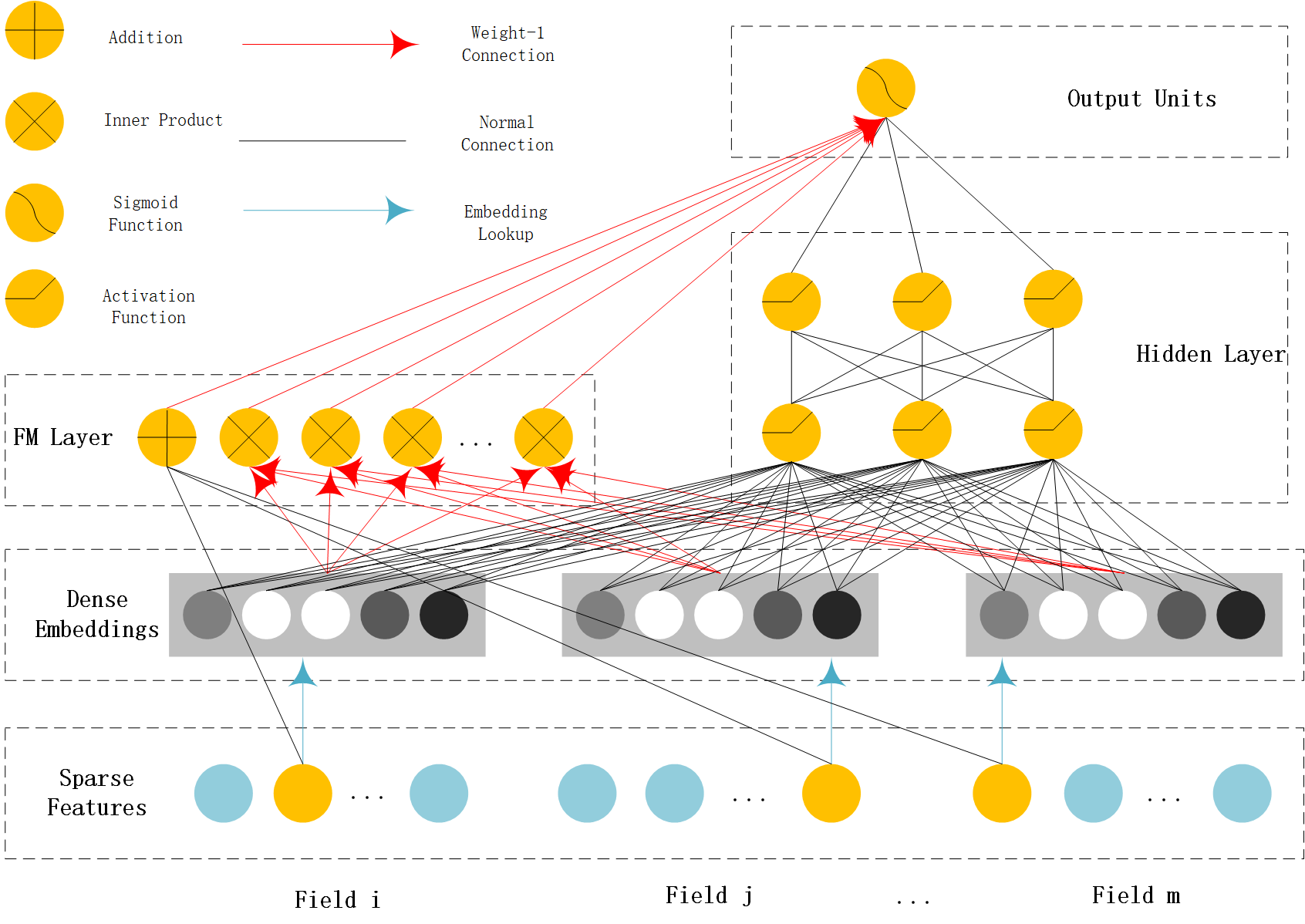
NFM (Neural Factorization Machine)¶
NFM use a bi-interaction pooling layer to learn feature interaction between embedding vectors and compress the result into a singe vector which has the same size as a single embedding vector. And then fed it into a MLP.The output logit of MLP and the output logit of linear part are added to get the prediction probability.
NFM Model API NFM Estimator API
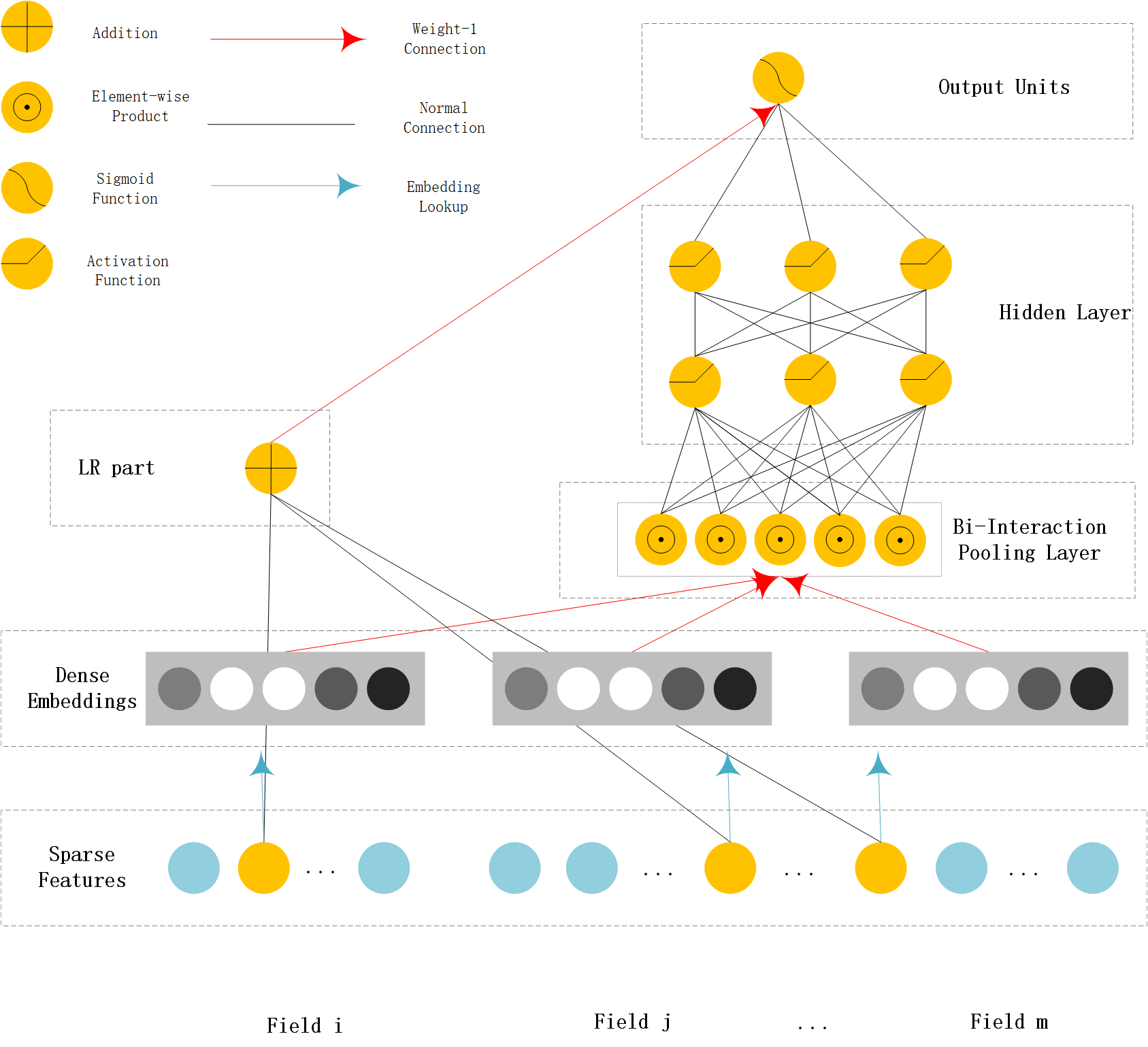
AFM (Attentional Factorization Machine)¶
AFM is a variant of FM,tradional FM sums the inner product of embedding vector uniformly. AFM can be seen as weighted sum of feature interactions.The weight is learned by a small MLP.
AFM Model API AFM Estimator API
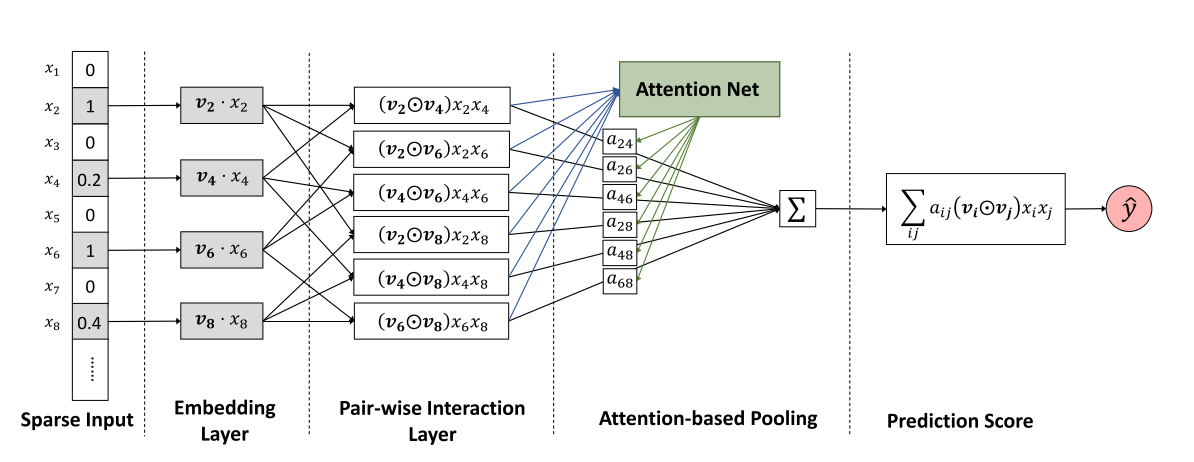
DCN (Deep & Cross Network)¶
DCN use a Cross Net to learn both low and high order feature interaction explicitly,and use a MLP to learn feature interaction implicitly. The output of Cross Net and MLP are concatenated.The concatenated vector are feed into one fully connected layer to get the prediction probability.
DCN Model API DCN Estimator API
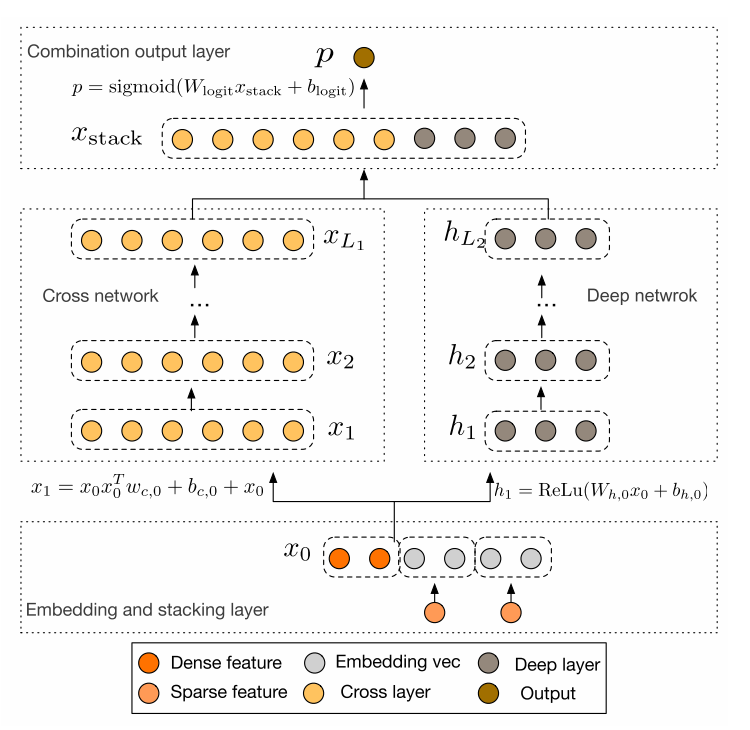
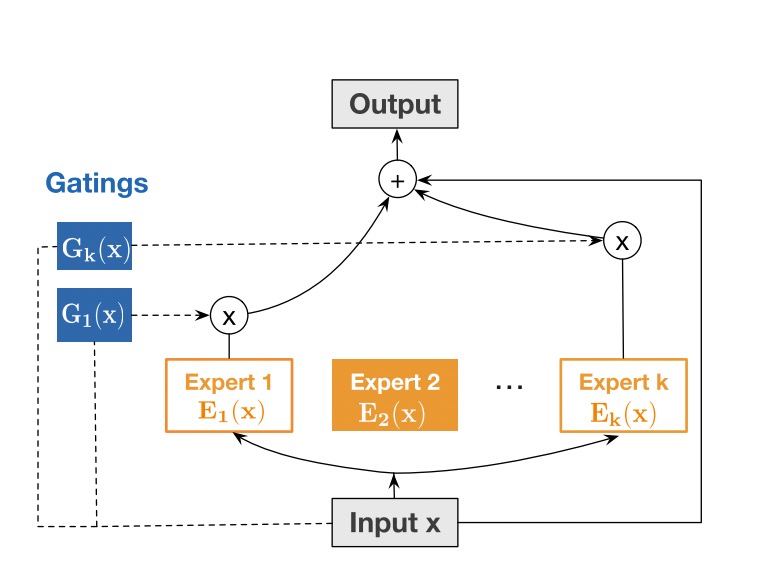
DCN-Mix (Improved Deep & Cross Network with mix of experts and matrix kernel)¶
DCN-Mix uses a matrix kernel instead of vector kernel in CrossNet compared with DCN,and it uses mixture of experts to learn feature interactions.
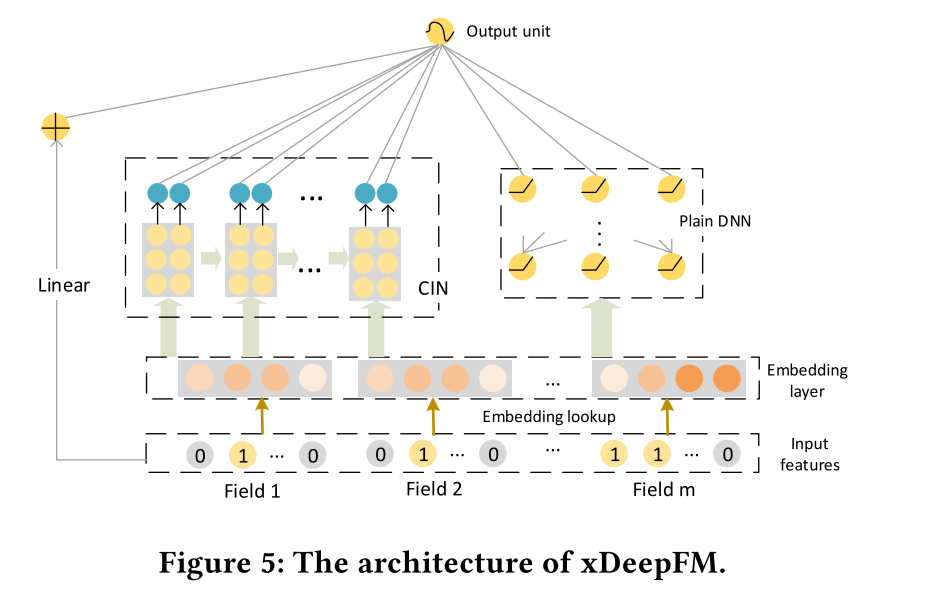
xDeepFM¶
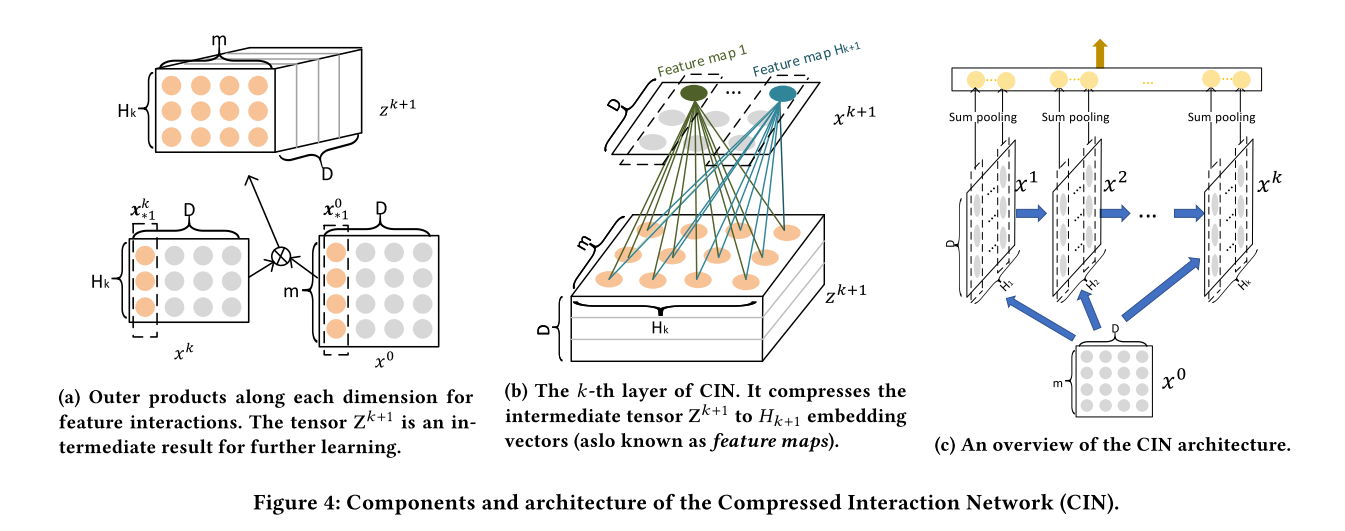
xDeepFM use a Compressed Interaction Network (CIN) to learn both low and high order feature interaction explicitly,and use a MLP to learn feature interaction implicitly. In each layer of CIN,first compute outer products between $x^k$ and $x_0$ to get a tensor $Z_{k+1}$,then use a 1DConv to learn feature maps $H_{k+1}$ on this tensor. Finally,apply sum pooling on all the feature maps $H_k$ to get one vector.The vector is used to compute the logit that CIN contributes.
xDeepFM Model API xDeepFM Estimator API
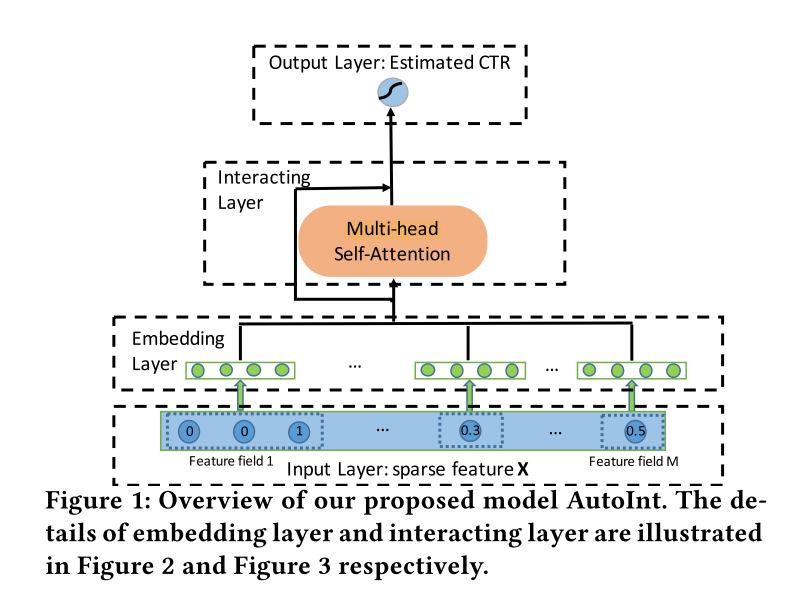
AutoInt(Automatic Feature Interaction)¶
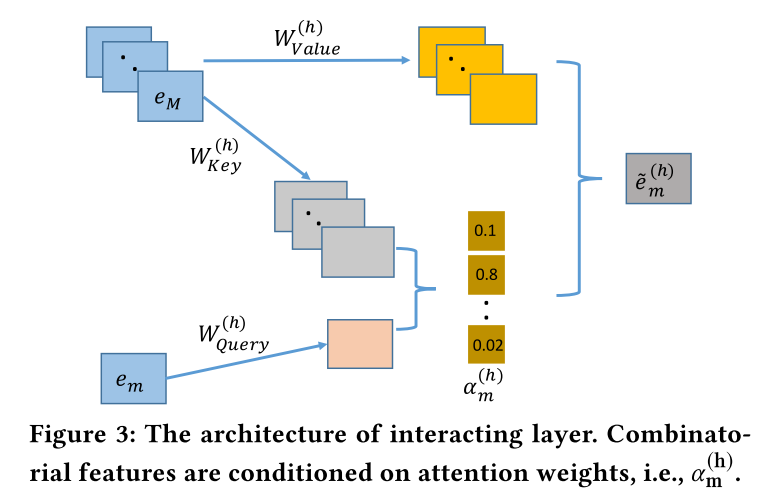
AutoInt use a interacting layer to model the interactions between different features. Within each interacting layer, each feature is allowed to interact with all the other features and is able to automatically identify relevant features to form meaningful higher-order features via the multi-head attention mechanism. By stacking multiple interacting layers,AutoInt is able to model different orders of feature interactions.
AutoInt Model API AutoInt Estimator API
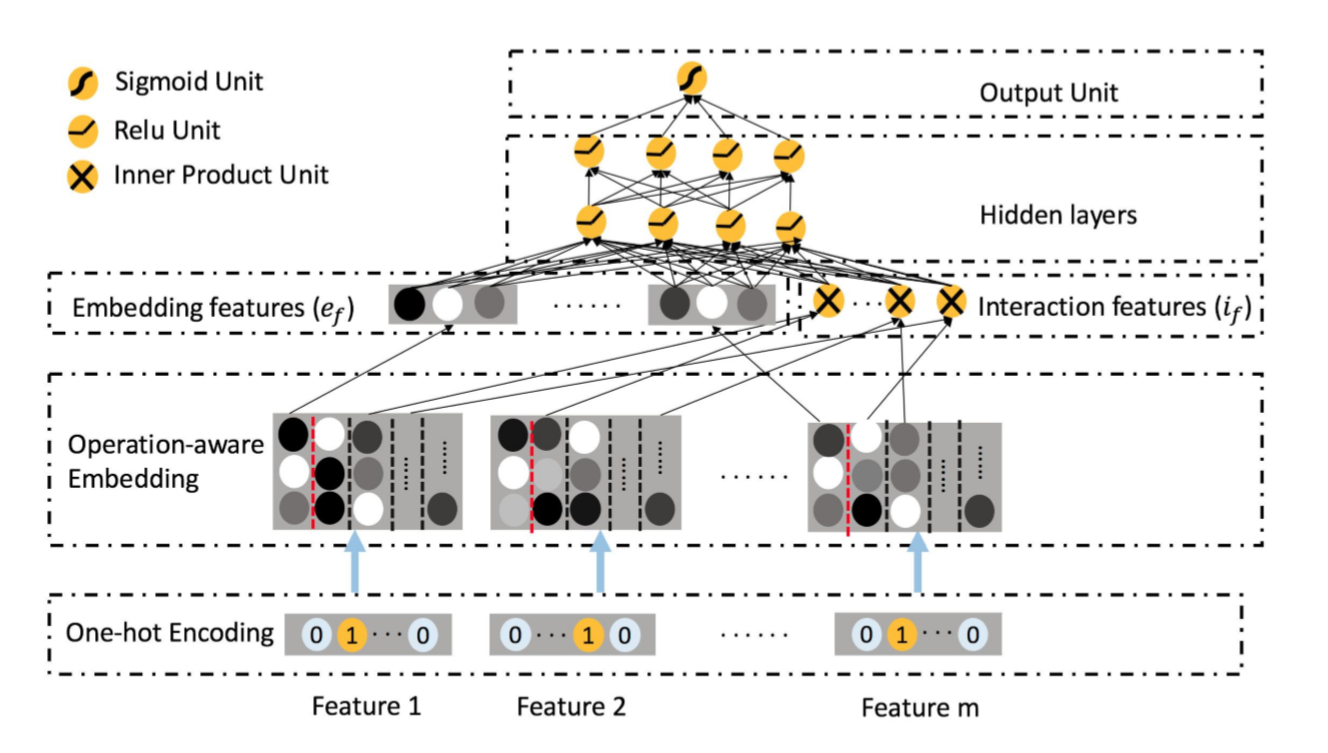
ONN(Operation-aware Neural Networks for User Response Prediction)¶
ONN models second order feature interactions like like FFM and preserves second-order interaction information as much as possible.Further more,deep neural network is used to learn higher-ordered feature interactions.
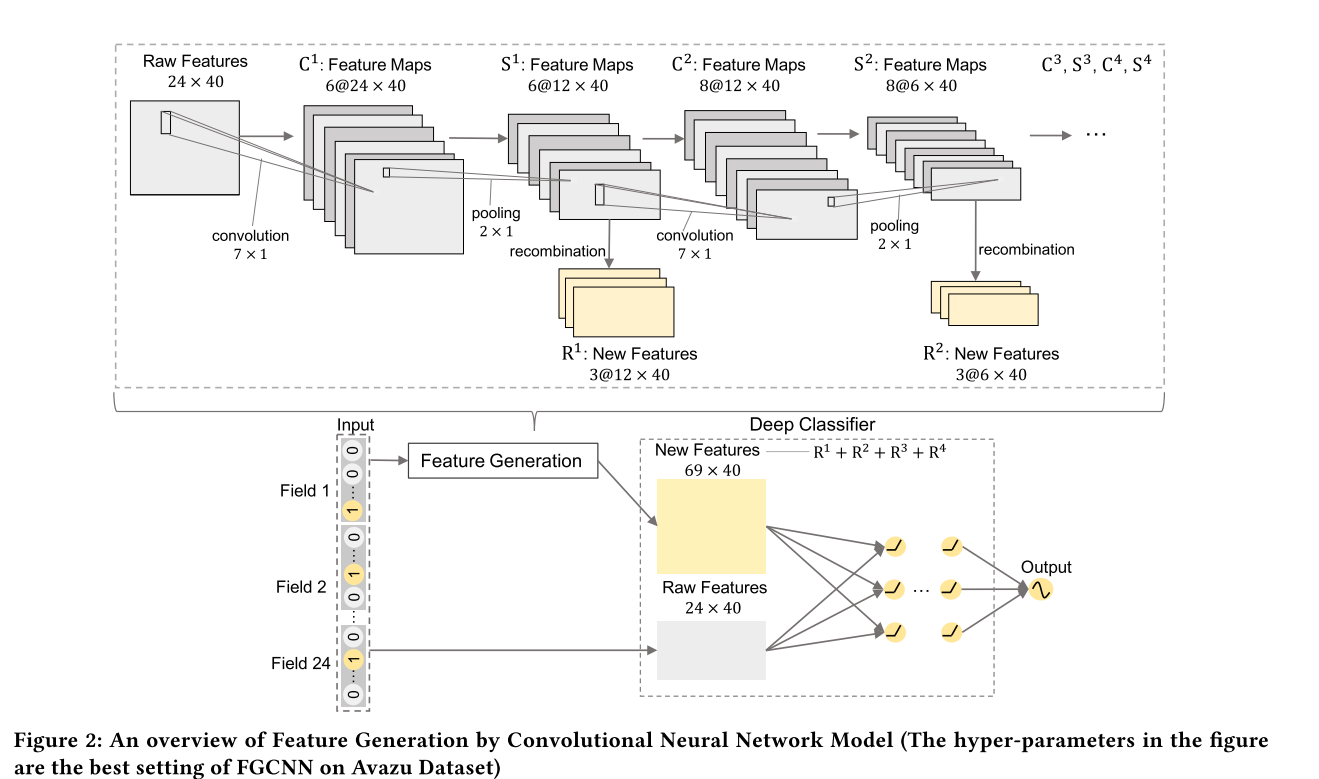
FGCNN(Feature Generation by Convolutional Neural Network)¶
FGCNN models with two components: Feature Generation and Deep Classifier. Feature Generation leverages the strength of CNN to generate local patterns and recombine them to generate new features. Deep Classifier adopts the structure of IPNN to learn interactions from the augmented feature space.
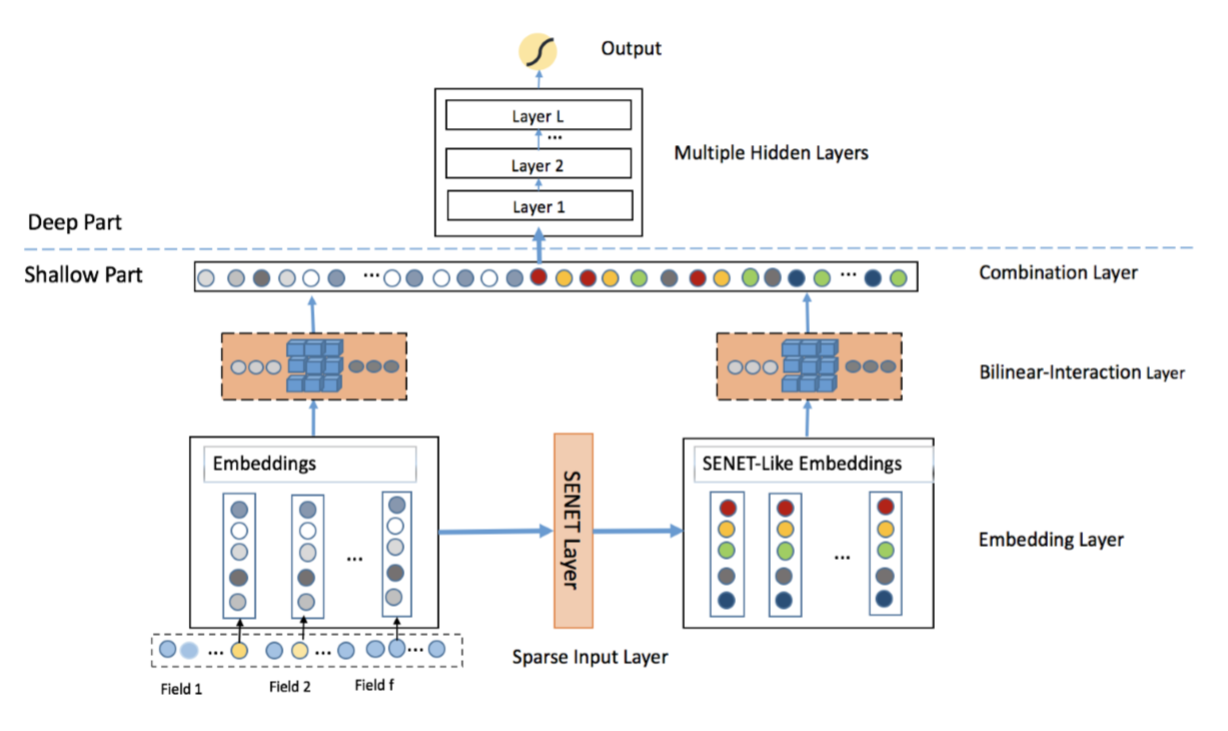
FiBiNET(Feature Importance and Bilinear feature Interaction NETwork)¶
Feature Importance and Bilinear feature Interaction NETwork is proposed to dynamically learn the feature importance and fine-grained feature interactions. On the one hand, the FiBiNET can dynamically learn the importance of fea- tures via the Squeeze-Excitation network (SENET) mechanism; on the other hand, it is able to effectively learn the feature interactions via bilinear function.
FiBiNET Model API FiBiNET Estimator API
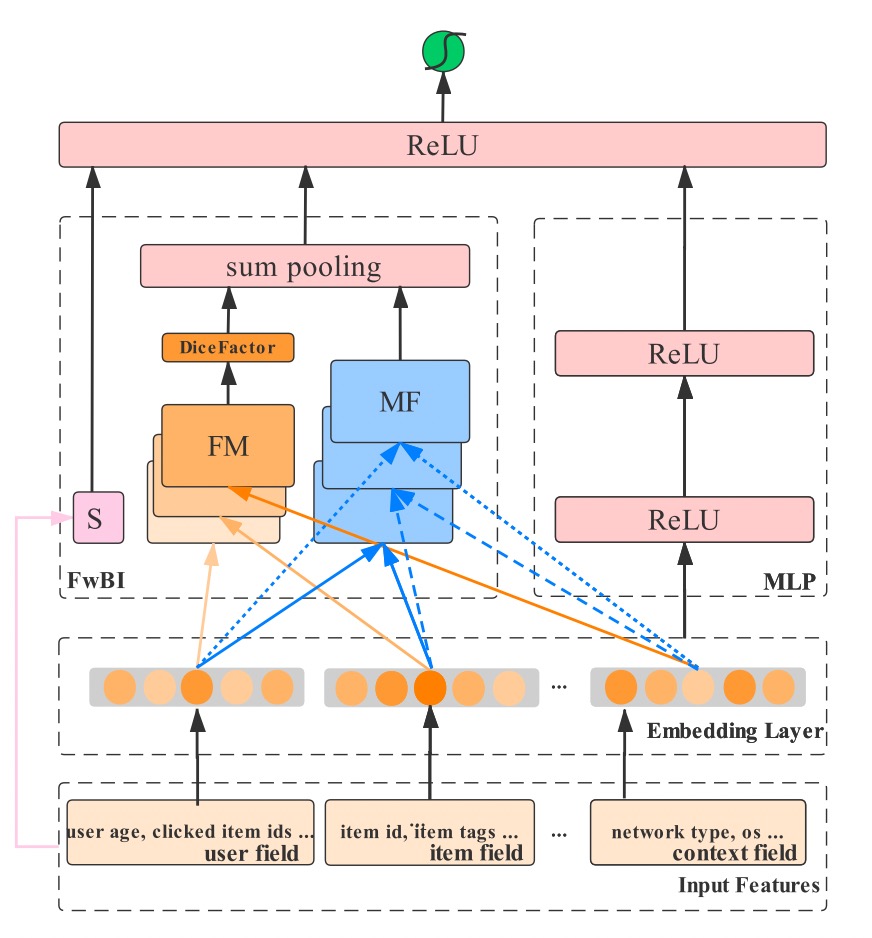
FLEN(Field-Leveraged Embedding Network)¶
A large-scale CTR prediction model with efficient usage of field information to alleviate gradient coupling problem.
IFM(Input-aware Factorization Machine)¶
IFM improves FMs by explicitly considering the impact of each individual input upon the representation of features, which learns a unique input-aware factor for the same feature in different instances via a neural network.
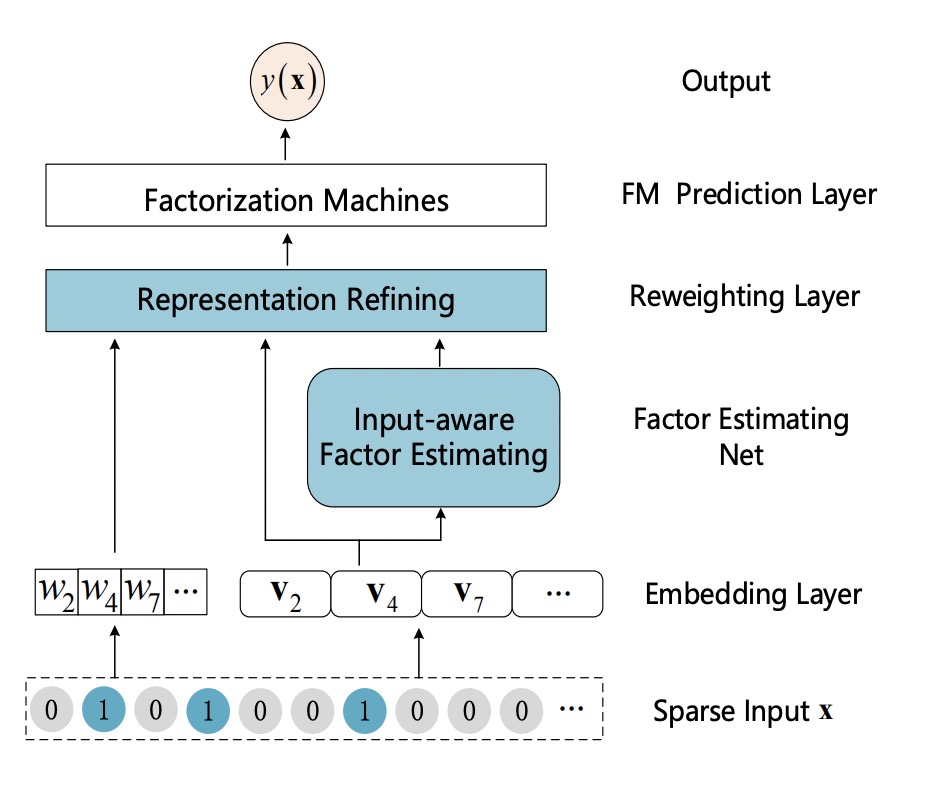
DIFM(Dual Input-aware Factorization Machine)¶
Dual Input-aware Factorization Machines (DIFMs) can adaptively reweight the original feature representations at the bit-wise and vector-wise levels simultaneously. DIFM Model API
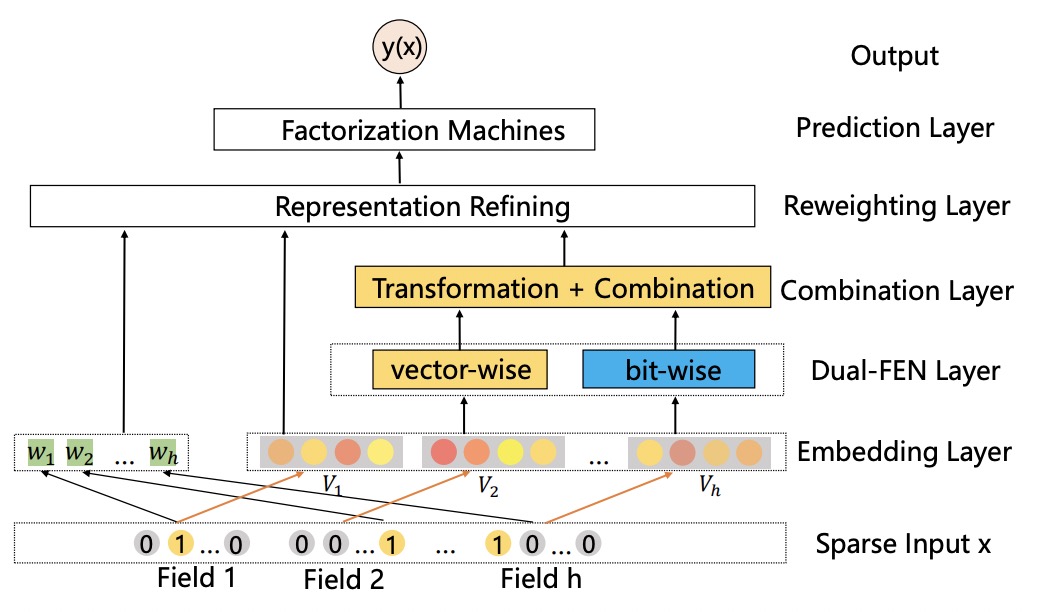
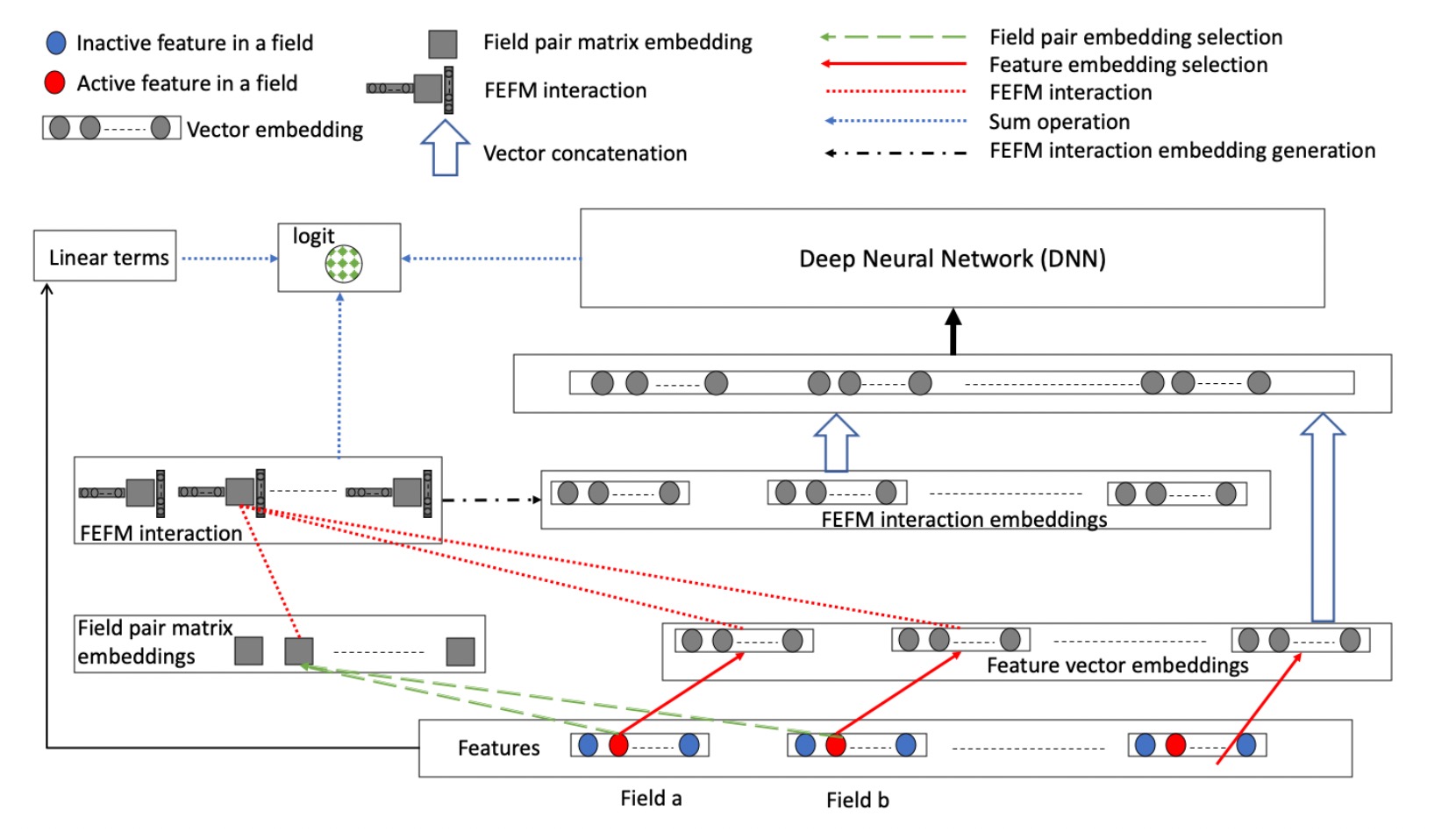
DeepFEFM(Deep Field-Embedded Factorization Machine)¶
FEFM learns symmetric matrix embeddings for each field pair along with the usual single vector embeddings for each feature. FEFM has significantly lower model complexity than FFM and roughly the same complexity as FwFM. DeepFEFM Model API
Sequence Models¶
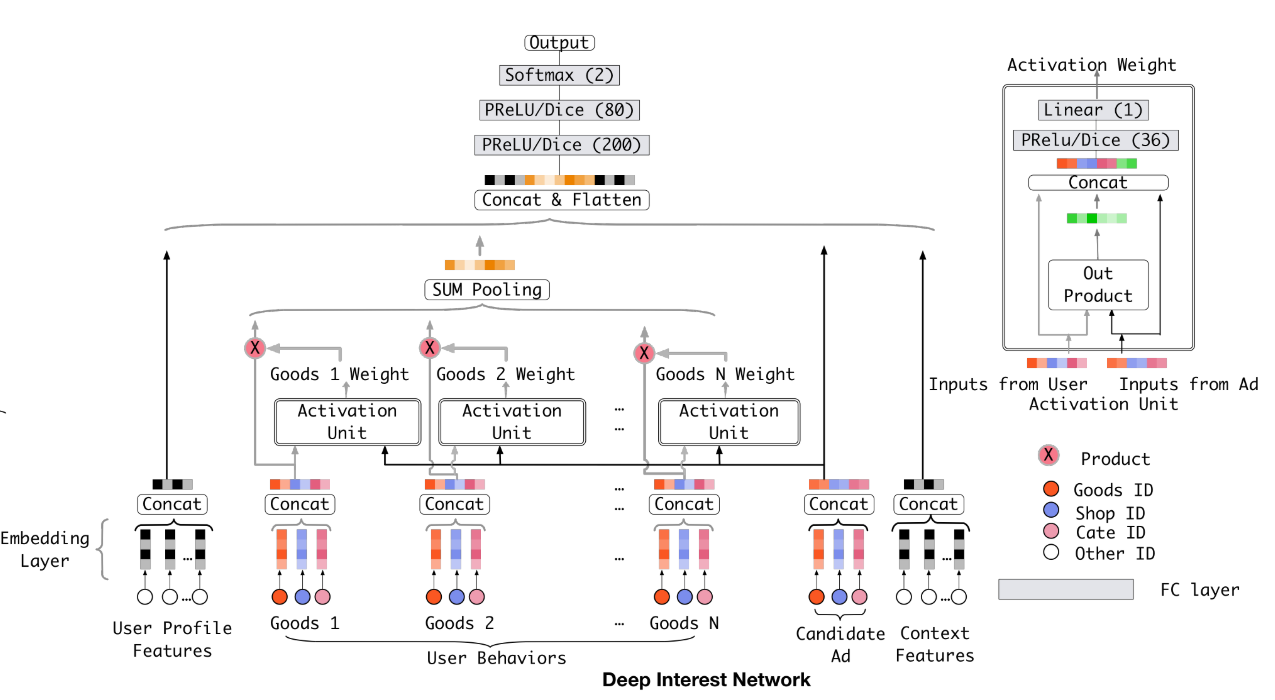
DIN (Deep Interest Network)¶
DIN introduce a attention method to learn from sequence(multi-valued) feature. Tradional method usually use sum/mean pooling on sequence feature. DIN use a local activation unit to get the activation score between candidate item and history items. User’s interest are represented by weighted sum of user behaviors. user’s interest vector and other embedding vectors are concatenated and fed into a MLP to get the prediction.
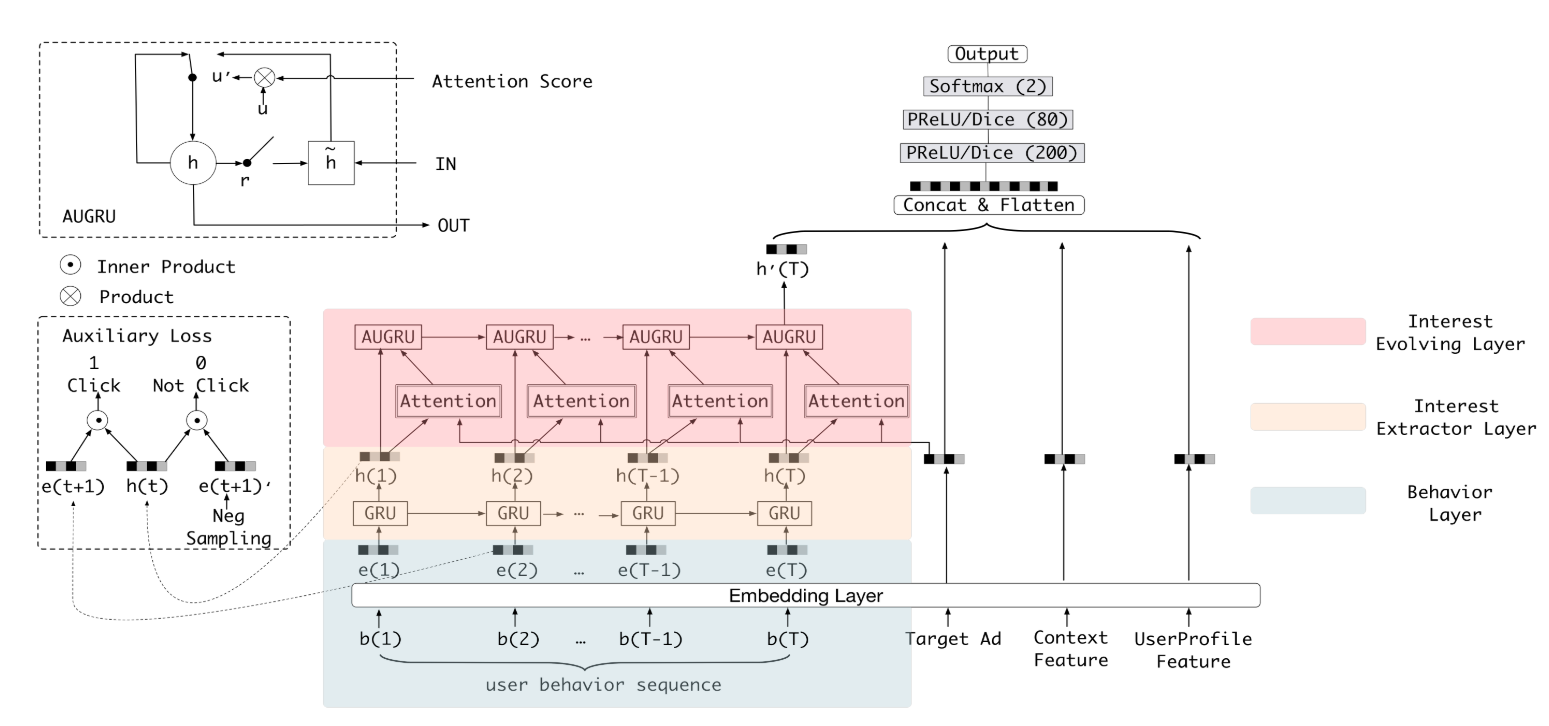
DIEN (Deep Interest Evolution Network)¶
Deep Interest Evolution Network (DIEN) uses interest extractor layer to capture temporal interests from history behavior sequence. At this layer, an auxiliary loss is proposed to supervise interest extracting at each step. As user interests are diverse, especially in the e-commerce system, interest evolving layer is proposed to capture interest evolving process that is relative to the target item. At interest evolving layer, attention mechanism is embedded into the sequential structure novelly, and the effects of relative interests are strengthened during interest evolution.
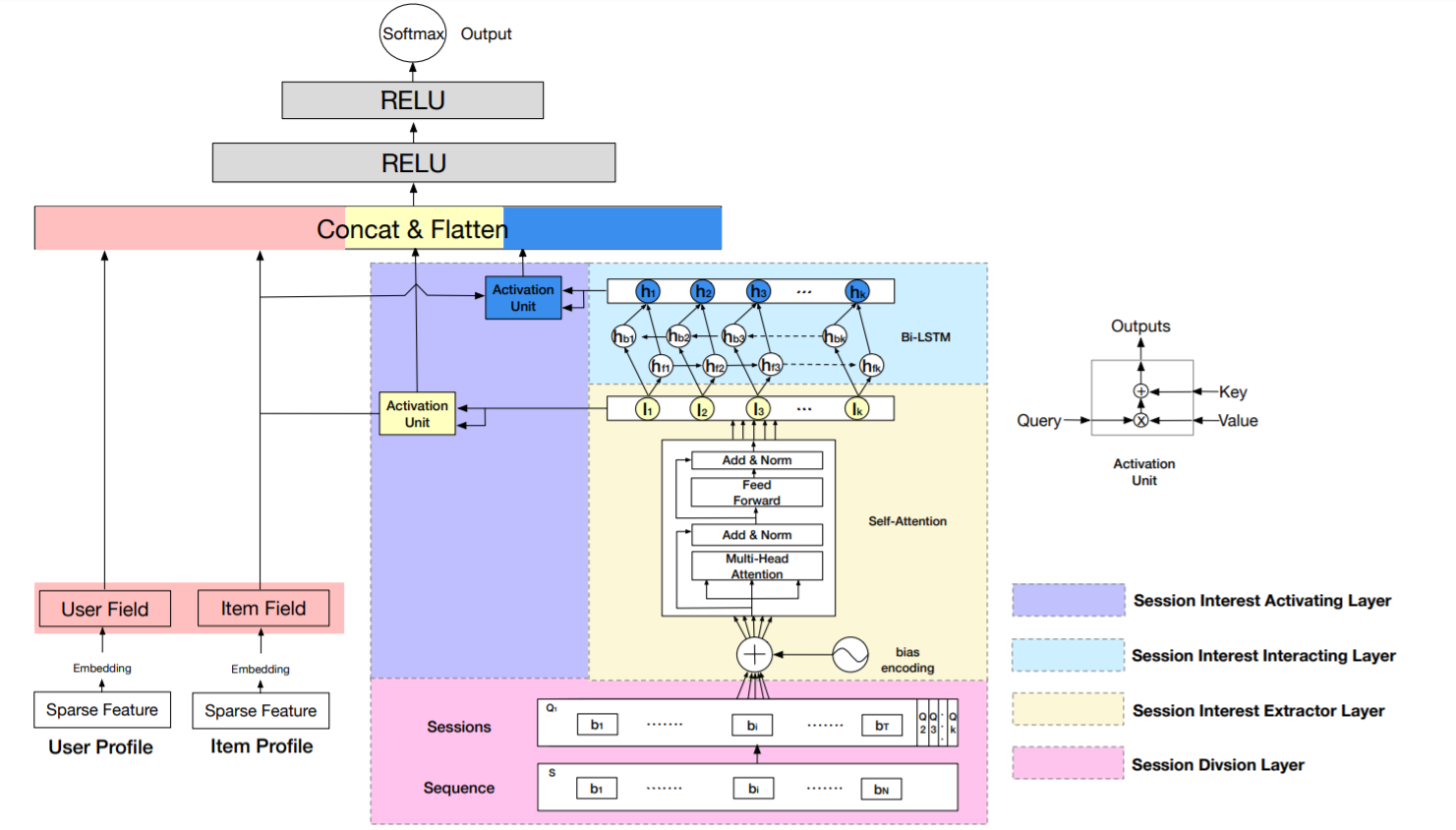
DSIN(Deep Session Interest Network)¶
Deep Session Interest Network (DSIN) extracts users’ multiple historical sessions in their behavior sequences. First it uses self-attention mechanism with bias encoding to extract users’ interests in each session. Then apply Bi-LSTM to model how users’ interests evolve and interact among sessions. Finally, local activation unit is used to adaptively learn the influences of various session interests on the target item.
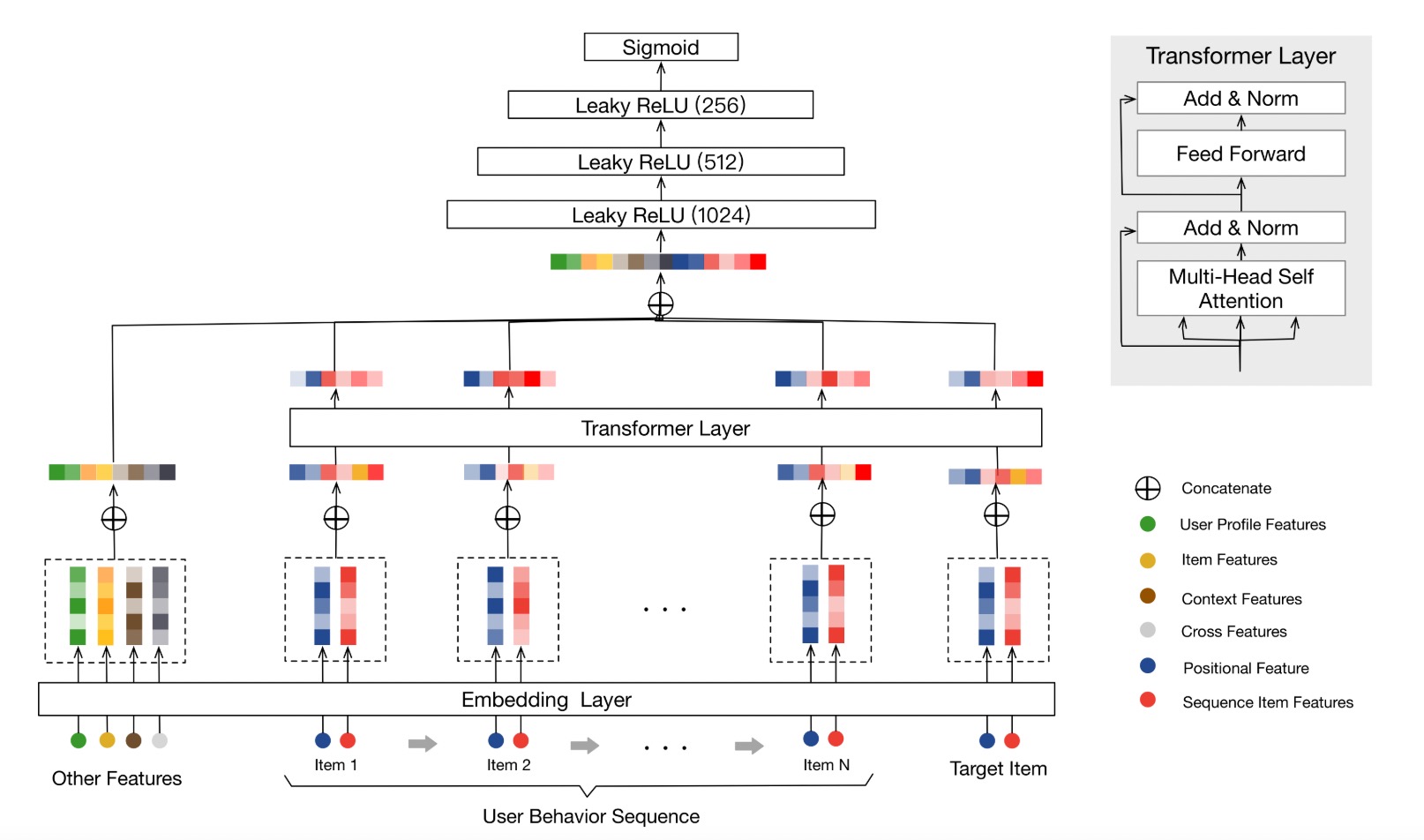
BST(Behavior Sequence Transformer)¶
BST use the powerful Transformer model to capture the sequential signals underlying users’ behavior sequences .
MultiTask Models¶
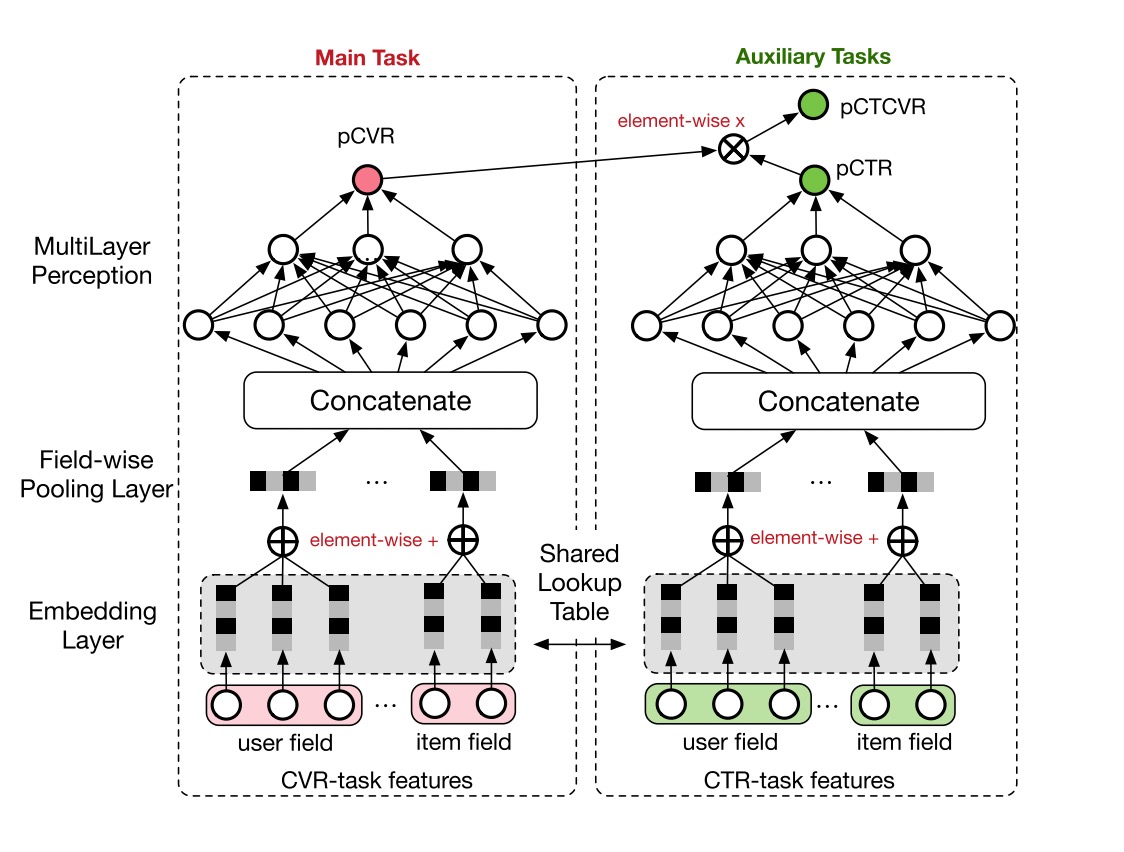
ESMM(Entire Space Multi-task Model)¶
ESMM models CVR in a brand-new perspective by making good use of sequential pattern of user actions, i.e., impression → click → conversion. The proposed Entire Space Multi-task Model (ESMM) can eliminate the two problems simultaneously by i) modeling CVR directly over the entire space, ii) employing a feature representation transfer learning strategy.
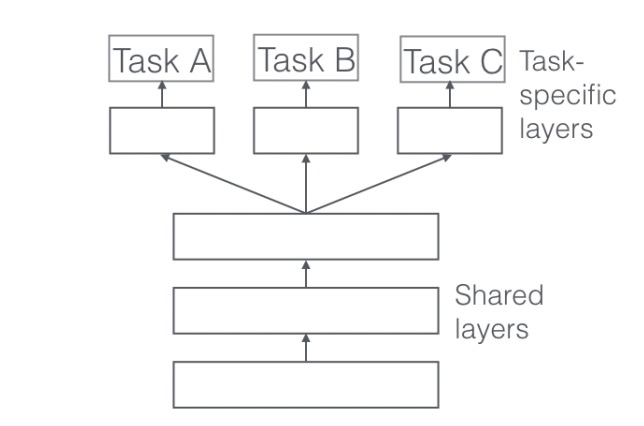
MMOE(Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts)¶
Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts (MMoE) explicitly learns to model task relationships from data. We adapt the Mixture-of- Experts (MoE) structure to multi-task learning by sharing the expert submodels across all tasks, while also having a gating network trained to optimize each task.
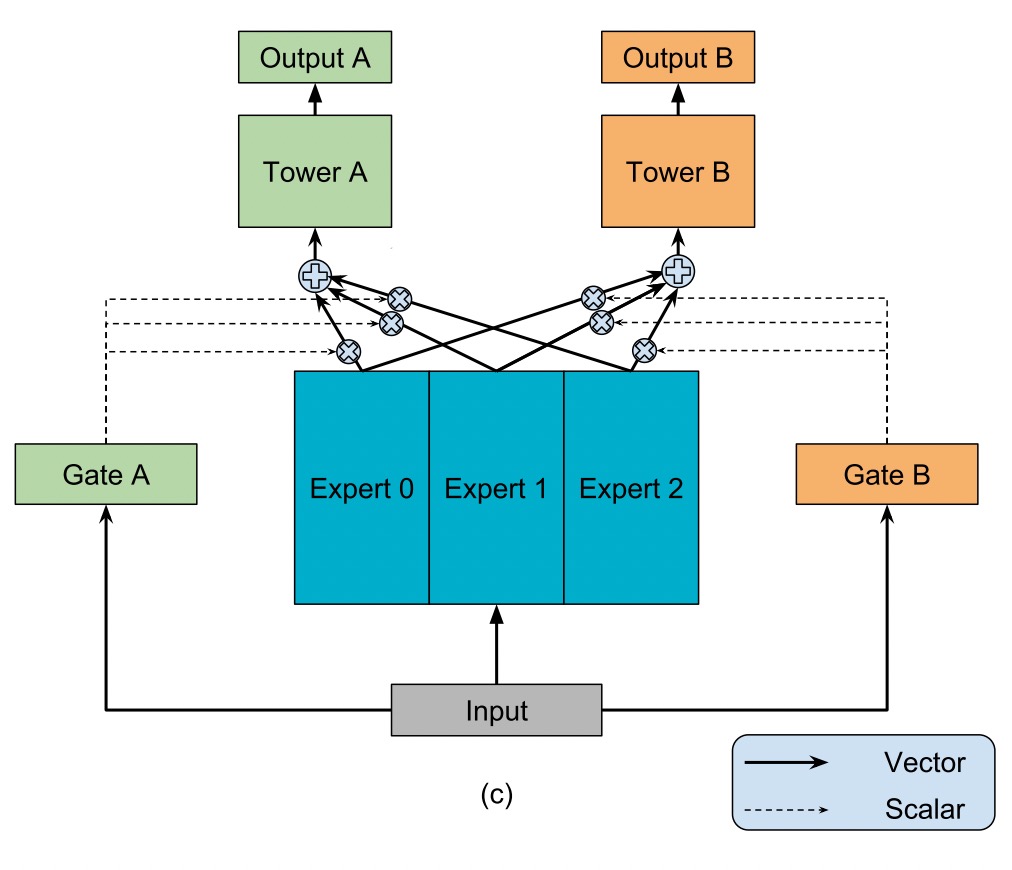
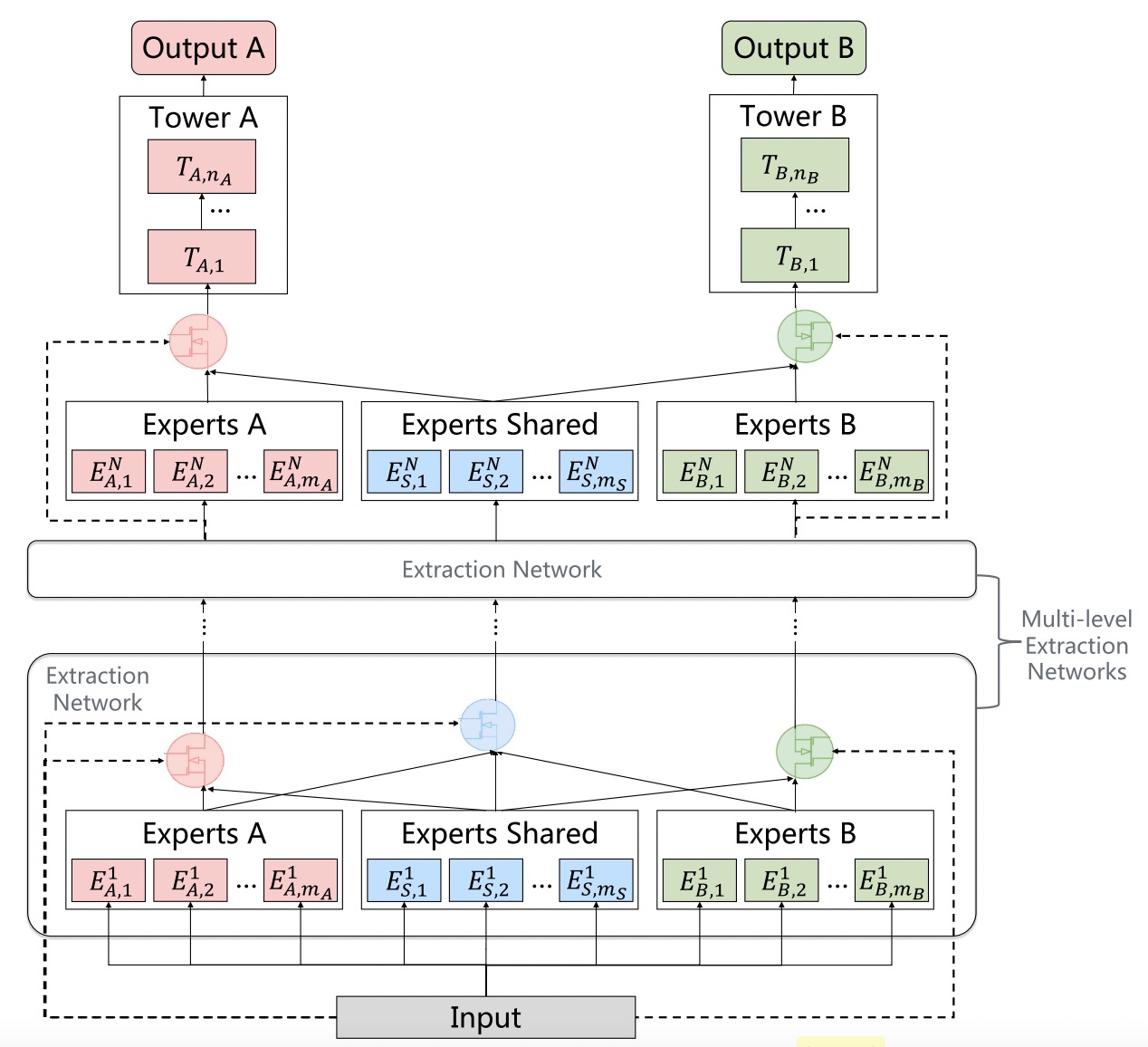
PLE(Progressive Layered Extraction)¶
PLE separates shared components and task-specific components explicitly and adopts a progressive rout- ing mechanism to extract and separate deeper semantic knowledge gradually, improving efficiency of joint representation learning and information routing across tasks in a general setup.